Understanding ETH: The Cryptocurrency Behind Ethereum
0019 ETH, a term that has become synonymous with Ethereum, represents the digital currency that powers the Ethereum blockchain. As you delve into the world of cryptocurrencies, understanding ETH is crucial. Let’s explore its history, characteristics, and potential future.
History of ETH
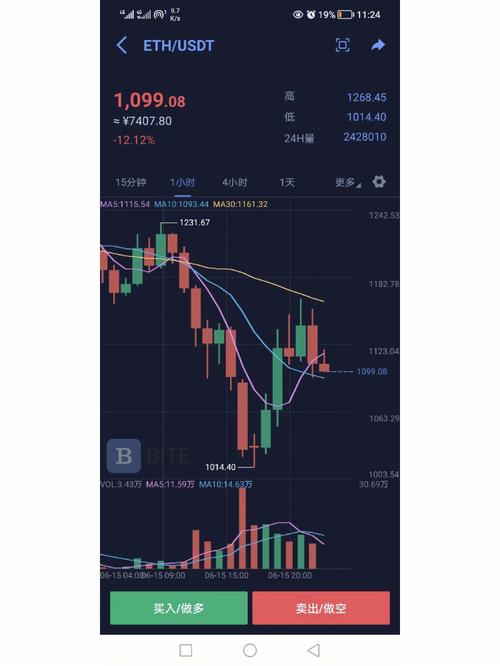
ETH was launched on July 30, 2015, with an initial price of $0.31. The cryptocurrency experienced a modest rise in value by the end of 2015, reaching a high of $2.8. However, it faced a downturn in early 2016, falling back to around $0.6. The year 2017 marked a significant surge in ETH’s value, with the price skyrocketing from $8 to $730 by the end of the year. This surge was primarily driven by the rise of ICO projects and decentralized applications (DApps) on the Ethereum platform. Unfortunately, 2018 saw ETH’s value plummet, falling from $1400 to $85 by the end of the year. The crash was attributed to factors such as the bursting of the ICO bubble, regulatory pressures, and technical challenges. In 2019, ETH’s value stabilized, fluctuating around $130. However, 2020 saw a resurgence in ETH’s value, reaching $730 by the end of the year. This was primarily due to the explosion of DeFi projects and the ETH2.0 deposit contract. In 2021, ETH’s value continued to rise, reaching an all-time high of $6300.
Characteristics and Advantages of ETH
ETH is not just a digital asset; it is the backbone of the Ethereum ecosystem. Here are some of its key characteristics and advantages:
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Decentralization | ETH is powered by the Ethereum blockchain, which is decentralized and has no central authority. All transactions and information are maintained and verified by nodes on the network. |
| Smart Contracts | Ethereum introduced smart contracts, allowing automated contract code execution on the blockchain without the need for intermediaries. This ensures reliability and fairness in contract execution. |
| Programmability | Ethereum enables developers to build and deploy various decentralized applications (DApps), catering to different industry needs and providing users with secure and transparent services. |
| Security | Ethereum employs cryptographic techniques and a decentralized ledger model to ensure the security of transactions and personal information, reducing the risk of hacking or data breaches. |
Applications of ETH
ETH has a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some examples:
-
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Ethereum’s smart contracts enable trustless financial services, such as decentralized exchanges, stablecoin issuance, and lending platforms.
-
Digital Asset Issuance and Management: Ethereum provides diverse tools for the issuance and management of digital assets, allowing various tokens to be created, destroyed, and transferred through smart contracts.
-
Internet of Things (IoT) Applications: Ethereum’s smart contract functionality can be integrated with IoT devices, enabling intelligent collaboration between devices and providing more convenient and secure IoT applications.
-
Decentralized Identity Verification: Ethereum’s smart contracts can be used to establish secure and privacy-protected digital identity solutions.
Future Outlook for ETH
The future of ETH is influenced by various factors, including market dynamics, regulatory changes, technological advancements, and community growth. While the cryptocurrency market faces challenges such as increasing mining difficulty and intense competition, there are also opportunities emerging. As more financial institutions enter the crypto space, and Ethereum continues to expand its technology and applications, the potential for ETH remains significant.
