Eth Current Gas Limit: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the Ethereum gas limit is crucial for anyone involved in the Ethereum ecosystem. The gas limit determines the maximum amount of computational work that can be performed in a single block. This article delves into the intricacies of the Ethereum gas limit, exploring its history, current status, and future implications.
What is the Ethereum Gas Limit?
The Ethereum gas limit is a fundamental concept in the Ethereum network. It represents the maximum amount of gas that can be consumed in a single block. Gas is the unit of measure used to pay for transactions and smart contract execution on the Ethereum network. Each operation, such as a transaction or a smart contract call, consumes a certain amount of gas.
History of the Ethereum Gas Limit
The Ethereum gas limit has evolved over time. Initially, the limit was set to 2,000,000 gas per block. However, as the network grew and more complex applications were developed, the gas limit was increased to accommodate the growing demand. In 2016, the gas limit was raised to 4,799,999 gas per block. This increase was aimed at preventing the network from becoming congested and ensuring that transactions and smart contracts could be executed efficiently.
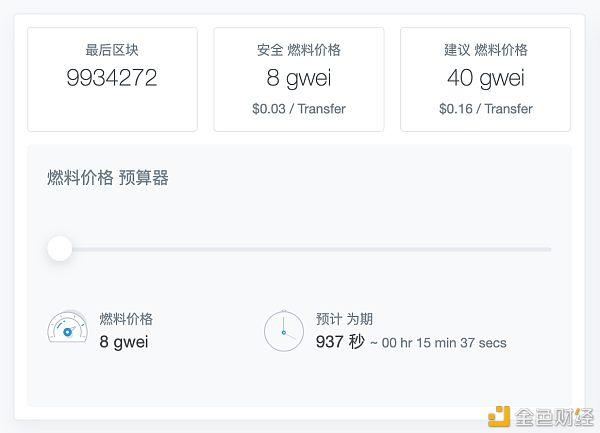
Current Status of the Ethereum Gas Limit
As of the latest update, the Ethereum gas limit stands at 12,000,000 gas per block. This limit has been in place since the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, which was completed in December 2020. The increase in the gas limit was part of the broader transition from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS). The new limit allows for more transactions and smart contracts to be processed in each block, improving the overall efficiency of the network.
Here is a table showing the historical gas limits of Ethereum:
| Year | Gas Limit |
|---|---|
| 2015 | 2,000,000 |
| 2016 | 4,799,999 |
| 2020 | 12,000,000 |
Impact of the Ethereum Gas Limit
The Ethereum gas limit has a significant impact on the network’s performance and user experience. A higher gas limit allows for more transactions and smart contracts to be processed in each block, reducing congestion and improving transaction speeds. However, it also increases the risk of centralization, as larger players may be able to control more of the network’s resources.
Future Implications of the Ethereum Gas Limit
The Ethereum gas limit is expected to continue evolving as the network grows and new technologies are developed. One potential future development is the implementation of sharding, which would allow the network to process more transactions and smart contracts simultaneously. This could lead to further increases in the gas limit, as well as the introduction of new mechanisms to manage the network’s resources more efficiently.
In conclusion, the Ethereum gas limit is a critical component of the network’s performance and user experience. Understanding its history, current status, and future implications is essential for anyone involved in the Ethereum ecosystem.
