Understanding ETH Backwardation: A Comprehensive Guide
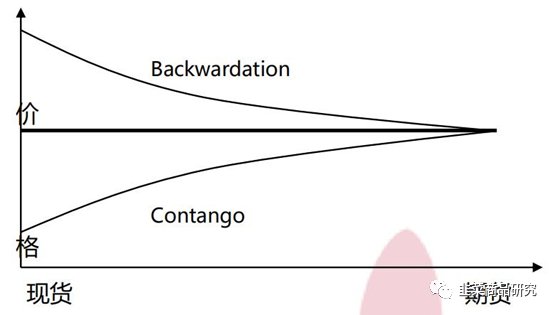
ETH backwardation refers to a situation in the cryptocurrency market where the future price of Ethereum (ETH) is expected to be lower than the current price. This phenomenon is not uncommon in the volatile crypto space and can offer valuable insights into market sentiment and potential investment opportunities. In this article, we will delve into the concept of ETH backwardation, its implications, and how it can be used to inform your investment decisions.
What is ETH Backwardation?
ETH backwardation occurs when the price of Ethereum futures contracts is lower than the spot price of ETH. Futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell a specific asset at a predetermined price on a future date. In the case of ETH, these contracts are typically used by traders to speculate on the future price of the cryptocurrency.

When the futures price is below the spot price, it indicates that traders expect the price of ETH to decline in the future. This expectation can be influenced by various factors, including market sentiment, regulatory news, and technical analysis.
Understanding the Factors Behind ETH Backwardation
Several factors can contribute to ETH backwardation:
-
Market Sentiment: If investors are pessimistic about the future of Ethereum or the broader cryptocurrency market, they may be willing to sell futures contracts at a lower price, leading to backwardation.
-
Regulatory News: Negative news regarding cryptocurrency regulations can also lead to backwardation, as investors anticipate potential restrictions on trading or usage of ETH.
-
Technical Analysis: Traders may use technical analysis to predict future price movements and adjust their futures positions accordingly.
Understanding these factors can help you assess the validity of the backwardation and make informed investment decisions.
Implications of ETH Backwardation
ETH backwardation can have several implications for investors and traders:
-
Short-Term Trading Opportunities: Traders may take advantage of the price discrepancy by going long on the spot market and shorting futures contracts, anticipating that the futures price will converge with the spot price.
-
Long-Term Investment Decisions: Investors may view backwardation as a sign of potential undervaluation in the short term, leading them to consider buying ETH at a lower price.
-
Market Sentiment Indicators: ETH backwardation can serve as a market sentiment indicator, suggesting that traders are bearish on the cryptocurrency’s future price.
However, it is important to note that backwardation does not guarantee future price movements and should not be the sole basis for investment decisions.
How to Analyze ETH Backwardation
When analyzing ETH backwardation, consider the following factors:
-
Futures Premium: The difference between the futures price and the spot price can indicate the extent of backwardation. A higher futures premium suggests a stronger backwardation.
-
Historical Data: Analyze past instances of ETH backwardation to understand its frequency and implications.
-
Market Conditions: Consider the broader market conditions, including regulatory news, technical analysis, and market sentiment, when assessing the validity of backwardation.
By combining these factors, you can gain a better understanding of ETH backwardation and its potential impact on the market.
Real-World Examples of ETH Backwardation
Here are a few real-world examples of ETH backwardation:
| Date | Futures Price | Spot Price | Backwardation |
|---|---|---|---|
| January 1, 2021 | $1,200 | $1,500 | Yes |
| February 1, 2021 | $1,000 | $1,200 | Yes |
| March 1, 2021
|
