Bioelectronics and Biosensors: A Comprehensive Guide
Bioelectronics and biosensors have emerged as revolutionary technologies in the field of healthcare and biotechnology. By harnessing the power of electronics and biology, these technologies have the potential to revolutionize the way we diagnose, monitor, and treat diseases. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of bioelectronics and biosensors, exploring their working principles, applications, and future prospects.
Understanding Bioelectronics
Bioelectronics refers to the integration of electronic devices with biological systems. These devices are designed to interact with biological tissues, cells, and molecules, enabling the monitoring and manipulation of biological processes. The primary goal of bioelectronics is to provide a non-invasive and minimally invasive approach to healthcare, thereby improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
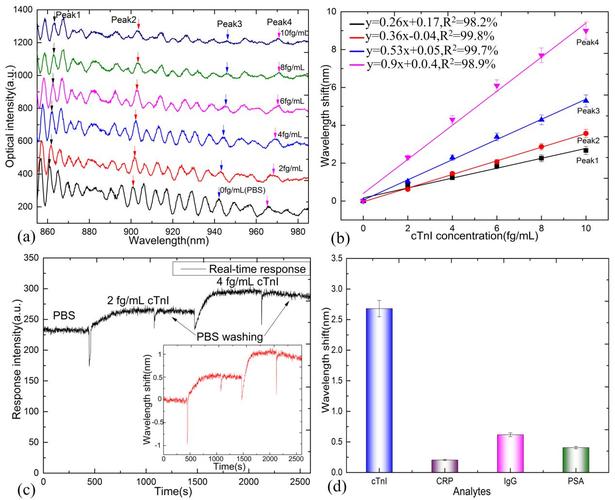
One of the key components of bioelectronics is the bioelectronic interface. This interface acts as a bridge between the electronic device and the biological system, facilitating the exchange of information. The bioelectronic interface can be designed to interact with various biological entities, including neurons, muscles, and organs.
How Bioelectronics Work
Bioelectronics devices typically consist of three main components: sensors, signal processing units, and actuators. Sensors are responsible for detecting biological signals, such as electrical activity, chemical changes, or mechanical forces. Signal processing units then analyze these signals and convert them into useful information. Finally, actuators are used to manipulate the biological system, such as delivering electrical stimulation or releasing therapeutic agents.
One of the most notable examples of a bioelectronic device is the neural interface. Neural interfaces are designed to interact with the nervous system, enabling the control of prosthetics, the treatment of neurological disorders, and the restoration of sensory functions. These devices can be used to restore motor control in individuals with paralysis, improve cognitive function in patients with neurological diseases, and even enable brain-computer interfaces for communication and control of external devices.
Applications of Bioelectronics
The applications of bioelectronics are vast and diverse. Here are some of the key areas where bioelectronics have made a significant impact:
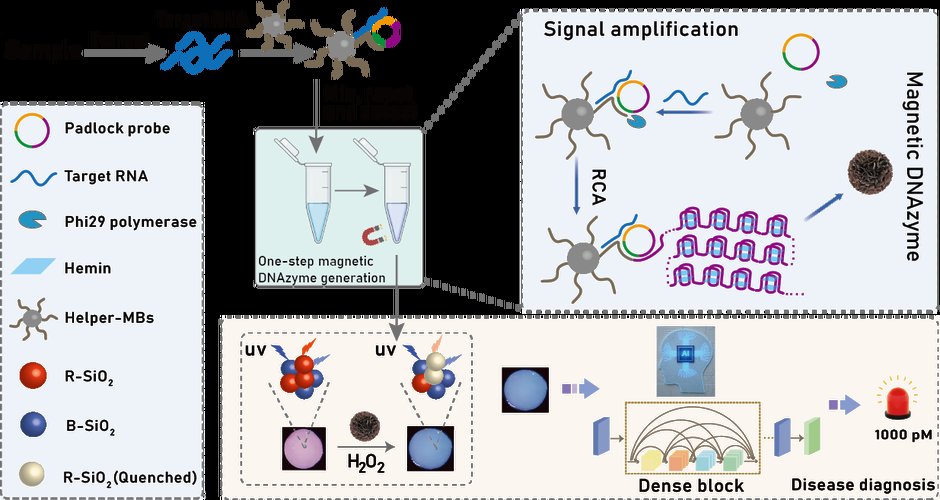
-
Neurology: Bioelectronics devices are used to treat neurological disorders such as epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, and chronic pain. These devices can deliver electrical stimulation to the brain or spinal cord, modulating neural activity and alleviating symptoms.
-
Cardiology: Bioelectronics devices are used to monitor and manage heart conditions, such as arrhythmias and heart failure. These devices can detect abnormal heart rhythms and deliver electrical therapy to restore normal heart function.
-
Diabetes: Bioelectronics devices are used to monitor blood glucose levels and deliver insulin therapy in individuals with diabetes. These devices can provide real-time data on glucose levels, enabling better control of blood sugar levels.
-
Wound Healing: Bioelectronics devices are used to promote wound healing by delivering electrical stimulation to the affected area. This stimulation can enhance the formation of new blood vessels and accelerate the healing process.
Understanding Biosensors
Biosensors are devices that detect and measure biological substances, such as proteins, DNA, and glucose. These devices are designed to be highly sensitive and selective, enabling the detection of low concentrations of target molecules. Biosensors have a wide range of applications in healthcare, environmental monitoring, and food safety.
Biosensors typically consist of three main components: a recognition element, a transducer, and a signal processing unit. The recognition element is responsible for binding to the target molecule, while the transducer converts the binding event into an electrical signal. The signal processing unit then analyzes the signal and provides a quantitative measurement of the target molecule.
Applications of Biosensors
Biosensors have numerous applications in various fields. Here are some of the key areas where biosensors have made a significant impact:
-
Healthcare: Biosensors are used for diagnostic purposes, such as detecting infectious diseases, monitoring patient vital signs, and assessing the effectiveness of treatments. They can also be used for personalized medicine, enabling the customization of treatments based on individual patient profiles.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Biosensors are used to monitor environmental pollutants, such as heavy metals, pesticides, and toxins. This information is crucial for ensuring the safety of water, air, and soil.
-
Food Safety: Biosensors are used to detect contaminants in food, such as bacteria, viruses, and allergens. This helps to ensure the safety and quality of food products.
